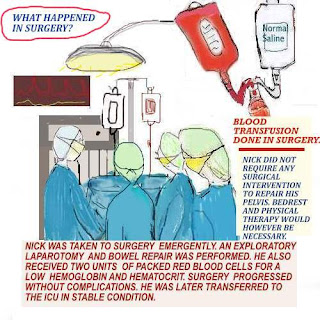
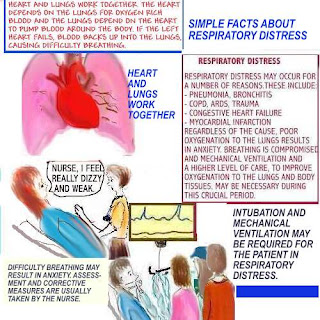
DEFINING TRAUMA CARE
How do you treat trauma?
When someone is involved in a traumatic event, whether car accident, burns, fall, impaled object, or cardiac event and more, the standard of care will depend on the severity of the injury or injuries.
Sometimes trauma may occur in a rural area or one where a higher skill level is not readily available. For this reason, services such as a helicopter service may be necessary to transfer the patient to a higher level of care.
Level II: Trauma center usually works in conjunction with a Level I trauma center and has 24-hour services. However, this level is not required to have a resident on call or a research program.
Level III: Does not have 24-hour service but has an intensive care and a surgical suite. Patients requiring a higher level of care would have to be transported to Level I or Level II.
Level IV: Works to stabilize injured patients who are far away and there are no other services.



 Updated 6/24 Trauma care
Updated 6/24 Trauma care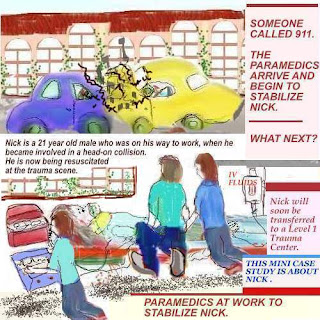



.JPG)









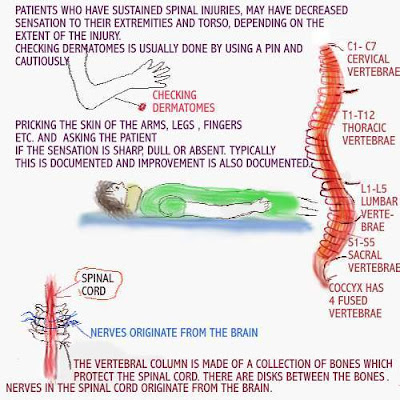


 Learn more, by clicking on the link below
Learn more, by clicking on the link below